
User Role Management: Complete Guide to Access Control in Your LMS
Master user role management in your learning management system. Learn how to configure administrators, managers, and learners with precise permissions for enhanced security and streamlined operations.
Managing a growing learning platform means juggling multiple user types—administrators creating courses, managers overseeing teams, and learners taking courses. Without proper access control, you risk security vulnerabilities, workflow confusion, and administrative headaches.
User Role Management solves this by giving each user precisely the permissions they need—no more, no less.
This guide explains how Konstantly's role management system provides the security, flexibility, and control your organization needs to scale efficiently.
What Is User Role Management?
User Role Management is a system that defines what actions different users can perform within your LMS platform.
Instead of giving everyone full access (security risk) or manually configuring each user's permissions (time-consuming nightmare), role-based access control (RBAC) assigns users to predefined roles with appropriate permissions.
Why Role Management Matters
Security: Prevents unauthorized access to sensitive data and critical functions Efficiency: Users see only relevant features, reducing confusion Compliance: Demonstrates proper data governance for audits Scalability: Onboard new users in seconds by assigning appropriate roles Accountability: Clear separation of responsibilities and audit trails
Real-World Example
Without role management:
- New hire accidentally deletes company-wide course catalog
- Manager can't assign courses to their team without admin help
- Course authors can't publish without admin approval
- Everyone sees every feature, creating overwhelming interface
With role management:
- Learners can only access assigned courses and personal settings
- Managers can assign courses and view team analytics
- Course authors can create and publish within their domain
- Administrators have full system control with audit logs
Konstantly's Pre-Configured User Roles
Konstantly offers three carefully designed roles out of the box, covering 90% of organizational needs.
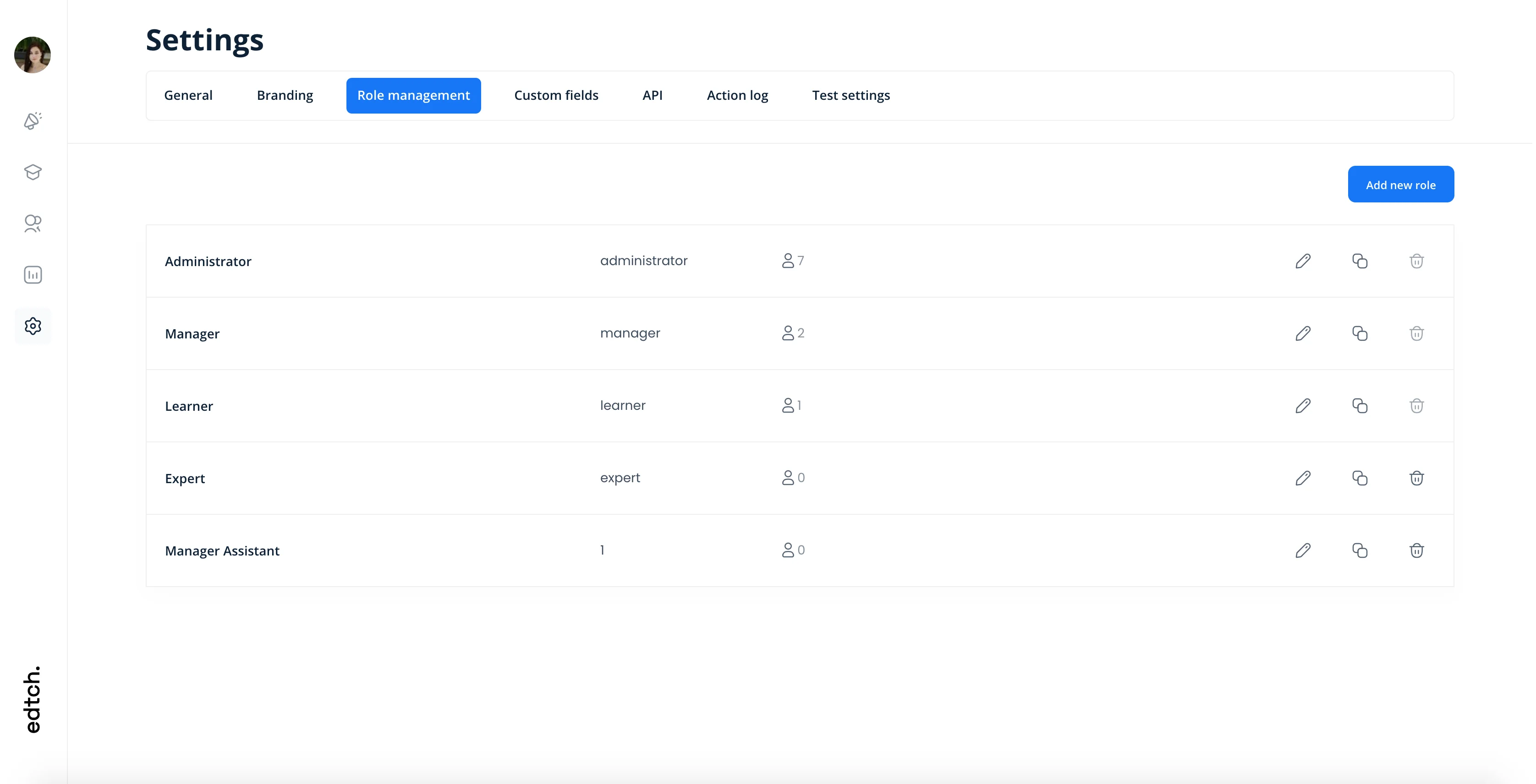 Role Management Interface
Role Management Interface
1. Administrator Role
Who needs it: IT administrators, L&D directors, platform owners
What they can do: ✅ Full platform access - Every feature, every setting, every user ✅ User management - Create, edit, delete, and assign roles ✅ Course management - Create, edit, publish, archive all courses ✅ Content creation - Access to AI course builder and all authoring tools ✅ Analytics & reporting - View all learner data, completion rates, engagement metrics ✅ Billing & subscription - Manage plans, payments, invoices ✅ Integrations - Configure SSO, API, webhooks, third-party apps ✅ Branding - Customize logos, colors, domains ✅ Settings - Modify all platform configurations
Use cases:
- Platform owner managing entire system
- IT administrator configuring SSO and integrations
- L&D director overseeing all training programs
Best practices:
- Limit to 1-3 people per organization (security principle of least privilege)
- Use strong passwords and enable 2FA
- Document all administrative actions
- Review admin access quarterly
2. Manager Role
Who needs it: Team leads, department heads, HR managers, training coordinators
What they can do: ✅ Team management - Assign users to courses, track team progress ✅ Course assignment - Enroll users in specific courses ✅ Analytics - View reports for assigned teams/users only ✅ Limited course creation - Create courses within their domain (if permitted) ⚠️ No global settings - Cannot modify platform-wide configurations ⚠️ No user creation - Cannot create new user accounts (admin-only) ⚠️ No billing access - Cannot view or modify subscription details
Use cases:
- Sales manager assigning product training to sales team
- HR lead tracking onboarding completion rates
- Department head monitoring compliance training progress
- Training coordinator scheduling and assigning courses
Best practices:
- Assign managers to specific teams or departments
- Grant course creation permissions only if needed
- Review manager activity monthly
- Provide manager training on analytics tools
3. Learner Role
Who needs it: Employees, customers, students, partners—anyone taking courses
What they can do: ✅ Access assigned courses - Take courses assigned by admins/managers ✅ View personal progress - See completion rates, scores, certificates ✅ Edit profile - Update name, email, password, photo ✅ Download certificates - Export earned credentials ⚠️ Cannot create courses - No authoring access ⚠️ Cannot view other users - Privacy by default ⚠️ Cannot access admin features - Simplified, focused interface
Use cases:
- Employee taking compliance training
- Customer learning product features
- Partner completing certification program
- Student accessing course materials
Best practices:
- Default role for all new users
- Minimal permissions reduce security risk
- Clean interface improves learner experience
- Monitor inactive learners for engagement
Custom User Roles: Precision Access Control
For organizations with complex hierarchies or specialized needs, Konstantly allows custom role creation (available on Business and Enterprise plans).
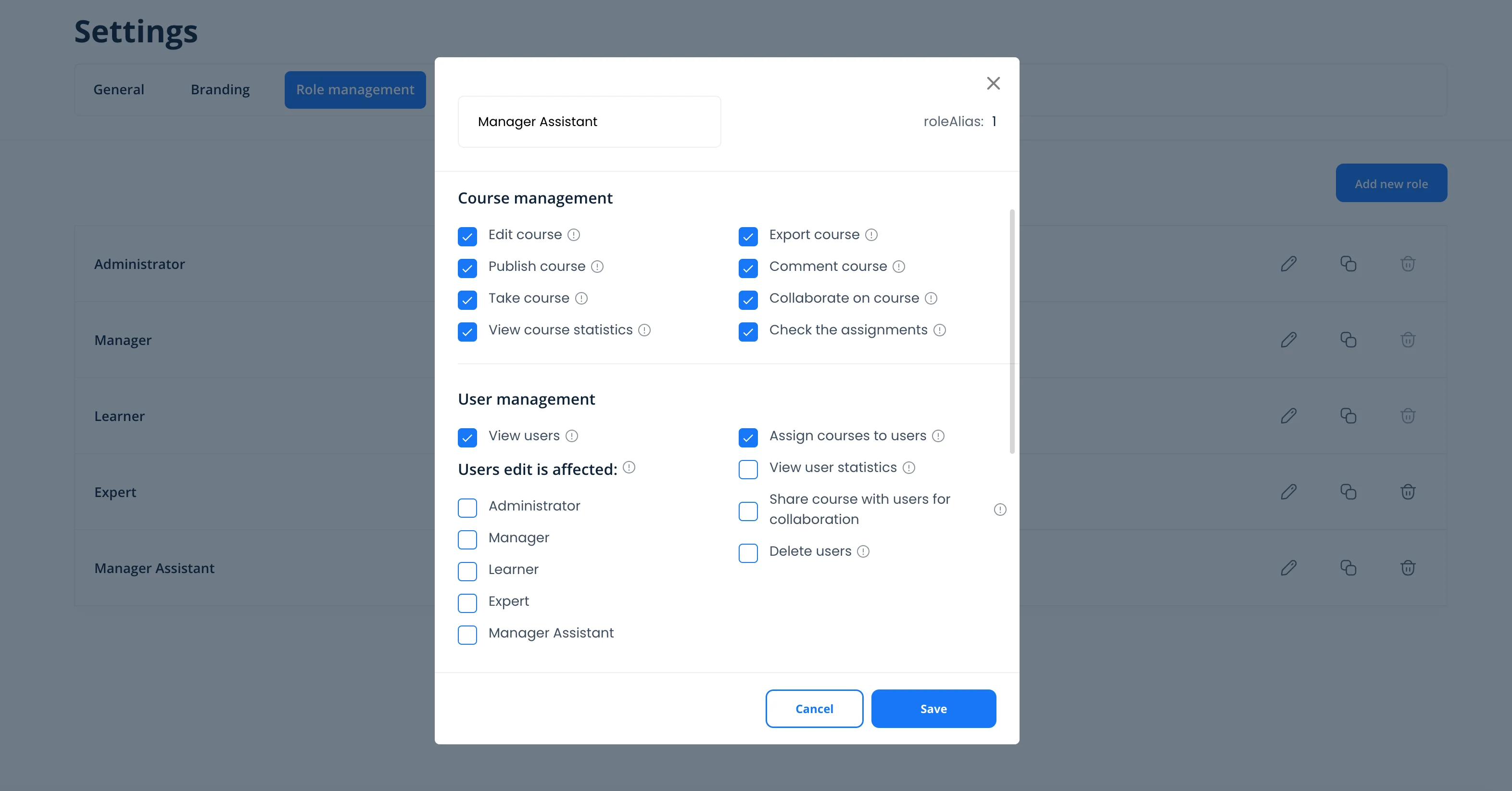 Custom Role Builder
Custom Role Builder
When You Need Custom Roles
Scenario 1: Course Authors (Non-Admins)
- Need: Create and edit courses, but not publish or manage users
- Custom role: "Course Creator" with authoring + preview, no publish/user management
Scenario 2: Compliance Officers
- Need: View all completion reports, cannot modify courses or users
- Custom role: "Auditor" with read-only analytics access
Scenario 3: External Contractors
- Need: Create courses in specific categories, limited platform access
- Custom role: "Contract Author" with scoped content creation
Scenario 4: Customer Success Team
- Need: Enroll customers in courses, view customer progress, no internal data access
- Custom role: "Customer Support" with external user management only
Creating Custom Roles in Konstantly
Step 1: Navigate to Settings → Role Management
Step 2: Click "Create Custom Role"
Step 3: Configure Permissions
You can grant/deny access across these permission categories:
User Management:
- View users
- Create users
- Edit users
- Delete users
- Assign roles
- Export user data
Course Management:
- View all courses
- Create courses
- Edit courses
- Publish courses
- Archive courses
- Duplicate courses
Content Authoring:
- Use AI course builder
- Upload media
- Create assessments
- Use question bank
- Create certificates
Team Management:
- Assign courses
- View team analytics
- Create groups
- Manage enrollments
Analytics & Reporting:
- View all reports
- View team reports only
- View own reports only
- Export analytics data
Platform Settings:
- Modify branding
- Configure integrations
- Manage billing
- Access API settings
Step 4: Name Your Role
Use clear, descriptive names:
- ✅ "Department Course Creator"
- ✅ "Customer Support Representative"
- ✅ "Compliance Auditor"
- ❌ "Role 1"
- ❌ "New Role"
Step 5: Assign Users
Add users to the new role immediately or save for later assignment.
Role-Based Enrollment: Advanced Control
Konstantly's role-based enrollment feature automatically assigns courses based on user roles.
 Role-Based Enrollment
Role-Based Enrollment
How It Works
Scenario: All new hires (Learner role) should automatically enroll in "Company Onboarding" course.
Configuration:
- Navigate to course settings
- Enable "Auto-enroll by role"
- Select "Learner" role
- Set enrollment trigger: "On user creation"
Result: Every new user assigned the Learner role instantly gets access to onboarding—zero manual work.
Use Cases for Role-Based Enrollment
New hire onboarding:
- Auto-enroll all Learners in foundational courses
- Managers automatically get "Leadership Fundamentals"
- Administrators get "Platform Admin Training"
Compliance training:
- All employees (across roles) auto-enroll in annual compliance courses
- Managers get additional "Management Compliance" training
Product updates:
- Sales team (Manager role) auto-enrolls in new product training
- Customer support gets feature update courses
Certifications:
- Role-specific certification paths
- Automatic re-enrollment for annual recertification
Managing User Roles: Best Practices
1. Follow the Principle of Least Privilege
Rule: Give users the minimum permissions needed to do their job.
Why: Reduces security risk, limits accidental damage, simplifies interface.
Example:
- ❌ Making everyone an admin "just in case"
- ✅ Granting manager role to team leads only
2. Regularly Audit Role Assignments
Frequency: Quarterly for small teams, monthly for enterprises
Checklist:
- Remove access for departed employees
- Downgrade permissions for role changes (manager → individual contributor)
- Upgrade permissions for promotions
- Review admin access (should be very limited)
Konstantly feature: Export user role report from Settings → Role Management
3. Document Role Responsibilities
Create internal documentation explaining:
- What each role can/cannot do
- When to request role changes
- Who approves role assignments
- Escalation process for access issues
Template:
Role: Manager
Permissions: Course assignment, team analytics
Cannot: Create users, modify billing, change platform settings
Request upgrade to Admin: Submit ticket to IT with manager approval
4. Train Users on Their Permissions
For Learners:
- How to access courses
- Where to find certificates
- How to update profile
For Managers:
- How to assign courses to team
- Reading analytics reports
- Requesting admin help when needed
For Admins:
- Complete platform training
- Security best practices
- Audit log review
5. Use Groups + Roles Together
Roles define what users can do. Groups define who users belong to.
Powerful combination:
- Create "Sales Team" group
- Assign Manager role to sales lead
- Manager can now assign courses to entire Sales Team group
Example hierarchy:
Organization
├── Sales Team (Group)
│ ├── Sales Manager (Manager role)
│ └── Sales Reps (Learner role)
├── Engineering Team (Group)
│ ├── Engineering Manager (Manager role)
│ └── Engineers (Learner role)
└── Admins (Group)
└── Platform Admin (Administrator role)
Security & Compliance Considerations
Data Privacy by Design
Konstantly's role management ensures privacy by default:
Learners cannot:
- See other users' personal information
- View other users' course progress
- Access company-wide analytics
Managers can only:
- View users assigned to their team
- See reports for courses they manage
- Access data relevant to their role
Administrators:
- Have full access with audit trail
- All admin actions logged
- Cannot delete audit logs (compliance requirement)
Compliance Features
GDPR Compliance:
- Users can request data export (personal data only)
- Admins can anonymize user data (course progress retained for analytics)
- Role-based data retention policies
FERPA Compliance (Education):
- Learner data invisible to other learners
- Managers see only aggregated data
- Individual records require admin access with audit trail
SOC 2 Compliance:
- Role changes logged with timestamp and user
- Permission changes tracked
- Quarterly access reviews recommended
Custom Field Permissions
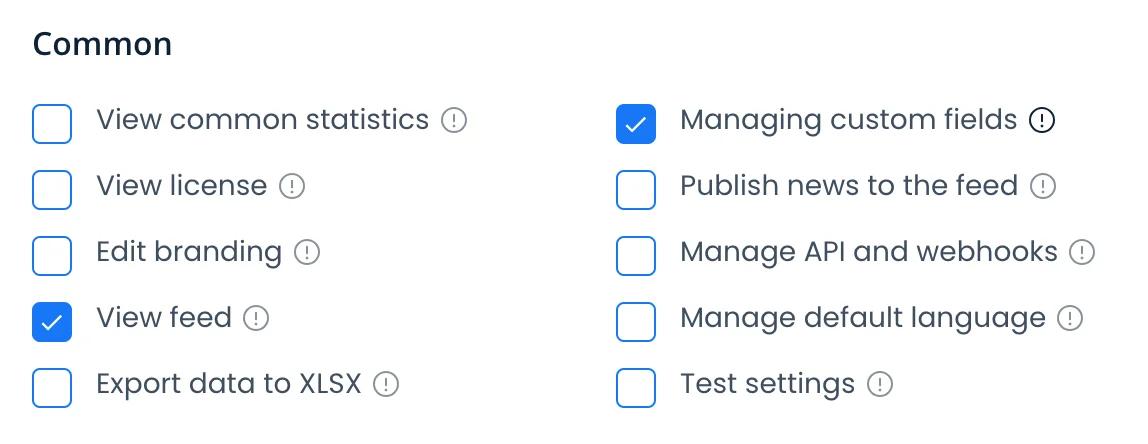 Custom Field Permissions
Custom Field Permissions
For sensitive custom fields (SSN, salary, performance reviews), Konstantly allows field-level permissions:
Example: "Employee ID" field
- Visible to: Administrator, HR Manager
- Hidden from: Learners, regular Managers
Configuration: Settings → Custom Fields → [Field Name] → Permissions
Common Role Management Scenarios
Scenario 1: Promoting User to Manager
Situation: Sarah was promoted from sales rep to sales manager. She needs to assign courses to her team.
Steps:
- Go to Settings → Users
- Find Sarah's account
- Change role from "Learner" to "Manager"
- Assign her to "Sales Team" group
- Sarah can now assign courses to sales reps
Result: Sarah keeps her learner access (can still take courses) but gains manager permissions for her team.
Scenario 2: External Course Creator
Situation: You hired a freelance instructional designer to create 10 courses. They shouldn't access user data or platform settings.
Steps:
- Create custom role: "External Course Creator"
- Grant permissions:
- ✅ Create courses
- ✅ Edit own courses
- ✅ Use AI builder
- ✅ Upload media
- ❌ Publish courses (requires admin approval)
- ❌ View users
- ❌ Access analytics
- Create user account with "External Course Creator" role
- Contractor creates courses, admin publishes after review
Result: Contractor can do their job without security risk.
Scenario 3: Department-Specific Access
Situation: Engineering manager should only see engineering team analytics, not company-wide data.
Steps:
- Create "Engineering Team" group
- Add all engineers to this group
- Assign manager role to engineering manager
- Configure manager scope: "Engineering Team" group only
- Manager sees only engineering analytics
Result: Each department manager sees only their team's data, ensuring privacy and focus.
Scenario 4: Temporary Admin Access
Situation: Regular manager needs temporary admin access to configure new integration, then should revert to manager role.
Steps:
- Grant temporary admin role
- Set calendar reminder for access review (1 week)
- Manager configures integration
- After completion, downgrade to manager role
- Document access change in audit log
Result: Minimal admin exposure, controlled access, proper documentation.
Advanced Role Features (Enterprise)
1. Role Hierarchies
Define parent-child role relationships:
Administrator (parent)
├── L&D Manager (inherits some admin permissions)
│ └── Course Creator (inherits manager view permissions)
└── IT Administrator (full technical access)
Benefit: Consistent permission inheritance, easier management at scale.
2. Time-Limited Roles
Grant temporary elevated permissions:
Use case: Contractor needs manager access for 3-month project.
Configuration:
- Assign "Manager" role
- Set expiration date: 3 months
- System automatically reverts to "Learner" after expiration
Benefit: Zero manual tracking, automatic access revocation.
3. Multi-Role Assignment
Assign multiple roles to single user:
Example: L&D manager who also takes courses
- Primary role: Administrator (platform management)
- Secondary role: Learner (personal development courses)
Benefit: Flexible access without creating complex custom roles.
4. Role-Based Notifications
Configure notifications based on roles:
Administrators receive:
- System health alerts
- Security notifications
- Billing reminders
Managers receive:
- Team completion notifications
- Overdue course alerts
- New user assignments
Learners receive:
- Course assignment notifications
- Deadline reminders
- Certificate earned confirmations
Implementing Role Management: Step-by-Step
Phase 1: Audit Current Users (Week 1)
- Export all users from your LMS
- Categorize by job function
- Document permission needs per category
- Identify who needs admin vs. manager vs. learner access
Deliverable: User role assignment spreadsheet
Phase 2: Configure Roles (Week 2)
- Use Konstantly's default roles for 90% of users
- Create 1-2 custom roles for unique needs
- Document each role's permissions
- Share with stakeholders for approval
Deliverable: Role permission matrix
Phase 3: Assign Roles (Week 3)
- Assign roles to all existing users
- Test permissions with sample users from each role
- Fix any permission gaps
- Communicate changes to users
Deliverable: All users have appropriate roles
Phase 4: Train Users (Week 4)
- Create role-specific training guides
- Host training sessions for admins and managers
- Send email instructions to learners
- Provide support during transition
Deliverable: User adoption of new role system
Phase 5: Monitor & Optimize (Ongoing)
- Review role assignments monthly
- Gather feedback on permission gaps
- Adjust custom roles as needed
- Audit admin access quarterly
Deliverable: Continuously improved role management
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Issue 1: User Can't Access Expected Feature
Symptom: Manager complains they can't view team analytics.
Diagnosis:
- Check user's assigned role
- Verify manager role includes analytics permission
- Confirm user is assigned to correct group/team
Solution: Either grant analytics permission to manager role, or create custom role with needed permissions.
Issue 2: Too Many Admins
Symptom: 10+ users have admin access.
Risk: Security vulnerability, accidental configuration changes.
Solution:
- Audit which users genuinely need admin access
- Create "Manager" or custom roles for others
- Downgrade non-essential admins
- Document admin access justification
Best practice: 1 admin per 50 users, maximum 3-5 admins per organization.
Issue 3: Custom Role Not Working as Expected
Symptom: Custom "Course Creator" role can't publish courses despite being granted permission.
Diagnosis:
- Review all permissions granted to role
- Check if "Publish" permission was actually enabled
- Test with admin account to confirm course is publishable
- Review role hierarchy (parent role might override)
Solution: Edit custom role, ensure "Publish courses" is checked, save, and test again.
Issue 4: Role Change Doesn't Take Effect
Symptom: Changed user from Learner to Manager, but they still can't assign courses.
Cause: User's browser cached old permissions.
Solution:
- Ask user to log out completely
- Clear browser cache
- Log back in
- Permissions should now reflect new role
Prevention: Konstantly automatically refreshes permissions every 5 minutes, but logout forces immediate refresh.
Role Management Checklist
Use this checklist to ensure proper role management implementation:
Initial Setup
☑️ Default roles configured (Admin, Manager, Learner) ☑️ Custom roles created for unique needs (if applicable) ☑️ All users assigned appropriate roles ☑️ Role permission matrix documented ☑️ Stakeholders trained on role system
Ongoing Maintenance
☑️ Monthly review of role assignments ☑️ Quarterly admin access audit ☑️ New user onboarding includes role assignment ☑️ Offboarding process includes role removal ☑️ Role change requests have approval workflow
Security
☑️ Admin access limited to 1-3 people ☑️ Admin accounts use strong passwords + 2FA ☑️ Audit logs reviewed monthly ☑️ Role changes tracked and documented ☑️ Data access follows principle of least privilege
Compliance
☑️ User data privacy enforced by roles ☑️ Field-level permissions configured for sensitive data ☑️ Audit trail enabled for all administrative actions ☑️ Role-based data retention policies documented ☑️ Compliance requirements mapped to role permissions
Conclusion: Security Meets Simplicity
Effective user role management is the foundation of a secure, scalable, and user-friendly learning platform.
With Konstantly's role management, you get:
✅ Security by default - Learners can't access admin functions ✅ Flexibility - Custom roles for unique organizational needs ✅ Simplicity - Pre-configured roles cover 90% of use cases ✅ Scalability - Onboard hundreds of users in minutes with role assignment ✅ Compliance - Audit trails, data privacy, and access control built-in
Key takeaways:
- Start simple - Use default roles (Admin, Manager, Learner) before creating custom roles
- Follow least privilege - Give users only the permissions they need
- Audit regularly - Review role assignments monthly, admin access quarterly
- Document everything - Role permissions, assignment process, approval workflow
- Train your users - Everyone should understand their permissions and boundaries
Ready to implement role management?
Start your free Konstantly account → (Includes role management on all plans)
View team management features →
Read the complete documentation →
Last updated: October 2024. Role management features available on all Konstantly plans. Custom roles require Business or Enterprise plan.